RESEARCHResearch Interests

RESEARCH INTERESTSExtractive Metallurgy
Extractive metallurgy is the branch of metallurgy concerned with the extraction of metals from their ores and the purification of those metals. It includes mineral processing, hydrometallurgy, pyrometallurgy, and electrometallurgy. Mineral processing involves crushing and grinding the ore to liberate the valuable minerals, while hydrometallurgy uses aqueous solutions to extract and purify the metal. Pyrometallurgy uses heat to extract and purify the metal, and electrometallurgy uses electricity to extract and purify the metal. The specific techniques used will depend on the type of ore and the desired end product.




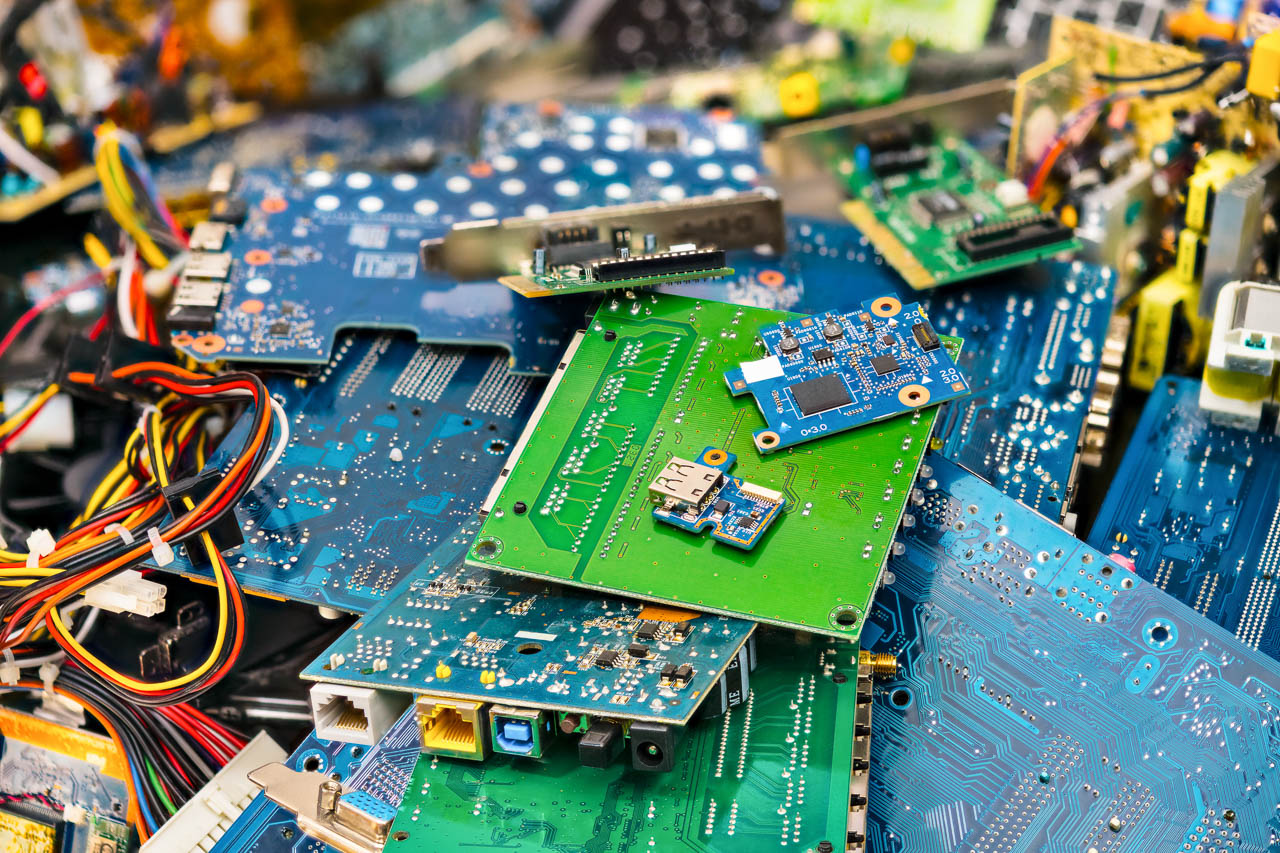
RESEARCH INTERESTSRecycling of Metallurgical Wastes
Recycling of metallurgical wastes refers to the process of recovering valuable metals and other materials from waste generated during the production of metals. This can include slags, dusts, sludges, and other byproducts of the smelting and refining process. Recycling these wastes can help reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills, conserve natural resources, and reduce the environmental impact of metal production. Techniques for recycling metallurgical wastes can include physical and chemical processing, such as crushing, grinding, leaching, and smelting.




RESEARCH INTERESTSSustainable Metallurgy
Sustainable metallurgy refers to the production of metals in a way that minimizes environmental impact and conserves natural resources. It involves the use of environmentally friendly techniques and technologies throughout the entire life cycle of the metal, from mining and extraction to refining, processing, and recycling. The goal of sustainable metallurgy is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, conserve water and energy, and minimize waste and pollution. This can be achieved through several methods, such as using renewable energy sources, recycling metals and metallurgical wastes, and developing new technologies that improve the efficiency and sustainability of the metal production process. Additionally, sustainable metallurgy also includes the responsible use of metals in products, and the ability to recycle them at end of life.




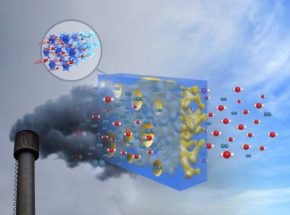
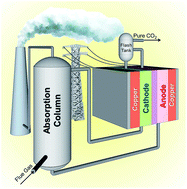
RESEARCH INTERESTSCO2 Capture
CO2 capture refers to the process of separating carbon dioxide (CO2) from other gases in industrial processes, such as those used in power plants, cement production, and other heavy industries. The captured CO2 can then be stored underground in geological formations or used in industrial processes such as enhanced oil recovery. The goal of CO2 capture is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, which are a major contributor to climate change.
There are several technologies available for CO2 capture, including:
- Pre-combustion capture, which involves separating CO2 from a fuel before it is burned.
- Post-combustion capture, which involves separating CO2 from flue gases after the fuel has been burned.
- Oxy-fuel combustion, which involves burning a fuel in a mixture of oxygen and recycled flue gases, resulting in a concentrated stream of CO2 that is easy to capture.
All of these technologies are still in development and are not yet widely used in industry due to high costs and lack of commercial readiness. However, it is a promising technology to reduce emissions from heavy industry sectors which are difficult to decarbonize.


RESEARCH INTERESTSSynthesis and Sintering of Advanced Ceramics
Synthesis of advanced ceramics involves the creation of ceramic materials through chemical or physical processes. This can include traditional ceramic forming techniques such as casting, pressing, and extrusion, as well as more advanced methods such as chemical vapor deposition and sol-gel processing.
Sintering is the process of heating a ceramic material to a temperature just below its melting point to cause it to become denser and stronger. This process is often used in the production of advanced ceramics, as it can improve the material’s mechanical properties and increase its resistance to wear and tear. Sintering can be done by various methods such as: spark plasma sintering, microwave sintering, hot isostatic pressing, pressureless sintering and so on.